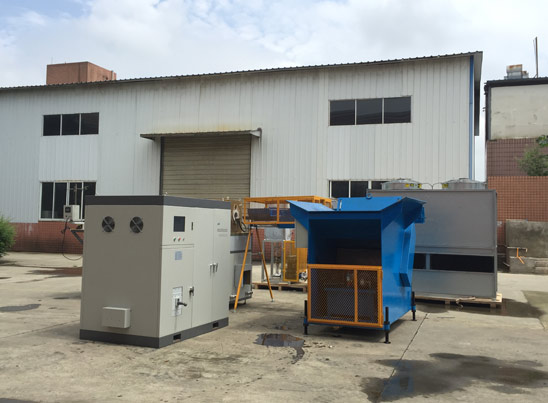
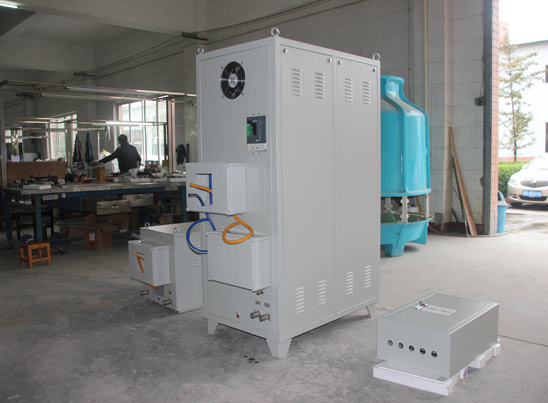
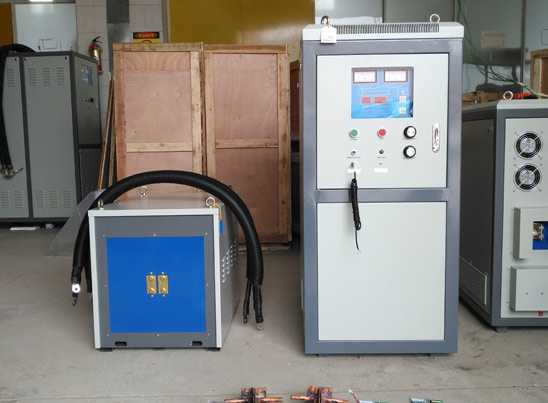
Due to its characteristics of being lightweight, high strength, corrosion-resistant, and having good formability, aluminum tubing is widely used in fields such as automotive manufacturing, chemical industry, agricultural irrigation, textiles, construction, and home assembly. As the demand for efficient welding processes in industry continues to rise, high-frequency induction heating is gradually replacing traditional argon arc welding, especially showing great potential in the field of aluminum tube welding. JKZ, as a company focused on the development of induction heating equipment, has accumulated rich technical experience and successful cases in this field.
Technical Challenges in High-Frequency Induction Heating Welding of Aluminum Tubes
Although high-frequency induction heating brings many advantages, welding aluminum tubes still faces several technical challenges:
High thermal conductivity and low melting point: Aluminum has high thermal conductivity and large heat capacity, making heat easily dissipate during the welding process, requiring rapid heating to complete the weld.
Easily oxidized: Aluminum easily forms an oxide film in the air, leading to welding inclusions and reduced joint strength.
Porosity issues: Molten aluminum can absorb a large amount of hydrogen, which if not controlled, can cause porosity in the weld.
No significant color change: During the melting process, it is difficult to visually judge the temperature change of aluminum, requiring high operational precision.
Technical Requirements for High-Frequency Induction Heating Equipment
To address the above challenges, the following requirements are put forward for high-frequency induction heating equipment:
Use high frequencies (usually above 100KHz, with some processes requiring 700-800KHz) to ensure a narrower heat-affected zone of the weld.
Ensure high power density to improve welding speed and quality.
The equipment oscillation circuit should have flexible load regulation, stable output power, and the anode DC voltage ripple factor controlled within 1%, ensuring the reliability of continuous production.
Key Measures for High-Frequency Induction Heating Welding of Aluminum Tubes
To ensure the welding quality of aluminum tubes, the following technical measures are usually adopted in the high-frequency induction heating process:
Increase frequency: Choose a frequency of 100KHz or even higher to enhance the concentration effect of the current in the weld area.
Increase output power: Ensure rapid heating and fusion to match the large heat capacity of aluminum.
Optimize circuit design: Ensure stable oscillation of the equipment, convenient load regulation, and adaptation to different pipe specifications.
Improve the cooling system: Due to the high thermal conductivity of aluminum, rapid cooling helps control the weld shape and reduce thermal stress.
As the trend of replacing steel with aluminum becomes more apparent, the demand for aluminum tubes is growing rapidly. In contrast, traditional argon arc welding has low welding speed and production efficiency, limiting capacity improvement. High-frequency induction heating welding, with its higher level of automation and faster production rhythm, is particularly suitable for mass and continuous production. As industrial manufacturing becomes more efficient and lightweight, the application value of high-frequency induction heating in aluminum tube welding is increasingly prominent. With advantages of high speed, low energy consumption, and being environmentally friendly and smokeless, this technology is becoming an important trend in the field of pipe welding. As a professional manufacturer in this field, JKZ will continue to promote the innovative application of induction heating technology, providing users with more efficient and intelligent welding solutions.

 en
en  cn
cn  jp
jp  ko
ko  de
de  es
es  it
it  ru
ru  pt
pt  th
th  vi
vi  pl
pl 

































 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  NO. 688th South Baoguang Road, Xindu District, Chengdu City, Sichuan Province, China
NO. 688th South Baoguang Road, Xindu District, Chengdu City, Sichuan Province, China